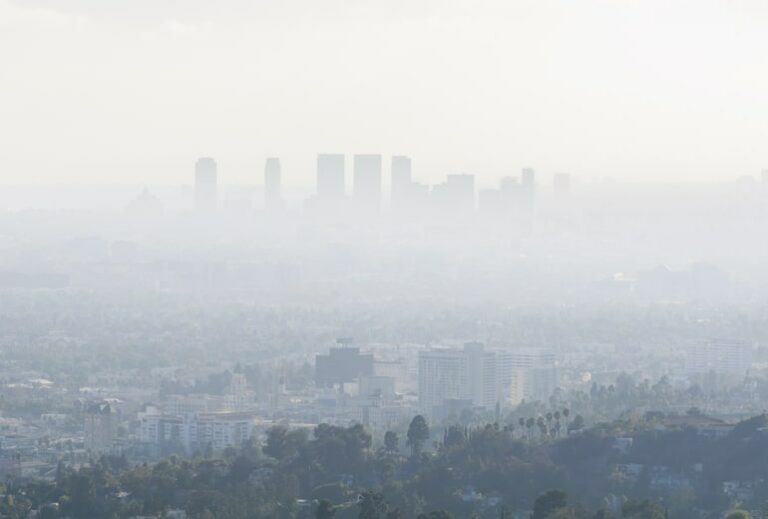
Air Pollution Levels: What Are We Really Breathing?

I recently moved from Utah County, Utah, to Park City, Utah. For one major reason: air quality, which is the subject of this post.
Park City is an expensive place to live, and a great place to spend time outdoors. But as the population of Utah County, my home for 33 years, grew, the air quality deteriorated as well. Especially during winter “inversions,” when warm air traps cold air in the valley. Until a major storm comes through, dirty air from cars and industry is trapped.
I also bought an electric car, to help do my part to reduce emissions in a part of the U.S. that sometimes has worse air than unregulated China. And I clean up my indoor air with portable, highly effective, and affordable Air Doctor filtration. So, obviously I feel strongly about this issue.
Everyday Air Pollution Exposure is Widespread
As much as 95 percent of the world’s population is exposed to dangerous levels of air pollution every day. Breathing in polluted air takes a toll on both public health and the environment, leading to widespread health epidemics, climate change, and a reduced quality of life.
In fact, over 200,000 people in the United States die each year directly from air pollution exposure. There is no way to calculate the effect of the hundreds of toxins found in air, on cancer incidence, but there are clear links.
There are three main types of these pollutants in our air as a result of human activities, toxic substance use, and industrial by-products.
Types of Air Pollutants
Particle Pollution
The air we breathe is filled with billions of microscopic particles. These airborne fragments are invisible to the naked eye, and measure to be 10 micrometers or smaller. Allergens, dust, metals, and minerals are some of the main types of particle pollutants.
While many of these occur naturally, pollution levels can spike in areas with a lot of activity like demolition sites or large construction projects. Lead, arsenic, and asbestos are among some of the most well known carcinogens that can be released during construction projects.

Some of the biggest culprits for particle pollution, aside from construction, are combustion from wildfires and vehicle exhaust, as well as agricultural burning.
Toxic Emissions
Toxic emissions are released into the air by a variety of domestic and industrial activities, including fire-burning, releasing smoke from factories, air conditioners, and vehicle exhaust. They are separated into four main categories: point, mobile, biogenic, and area.
- Point emissions are produced by factories, power plants, and other stationary facilities that produce pollution. This is a result of heating, incinerating, generating power, or other processes involved in manufacturing.
- Mobile sources are typically types of vehicles or modes of transportation. On-road mobile sources are typical vehicles like cars, trucks, motorcycles, and buses. Off-road sources include more of a variety, from airplanes, to lawnmowers, to boats, to farming equipment.
- Biogenic emissions are brought on by natural sources in the environment. The most common are plants and trees, but other sources are volcanic emissions, sea salt, and lightning storms.
- Area emissions are specific to a location that is known for poor air quality. This can be caused by a few factors like active forest fires, railway stations, or expansive worksites.
Everyday activities like lighting a fireplace, using a gas stove, or turning on air conditioning contribute a great deal to worsening air quality. Normal practices like these can produce toxic emissions like nitric acid, aerosol, and carbon compounds that play their part in contributing to global warming.
Ozone
While the upper ozone layer protects us from harmful UV rays, ozone in the lower atmosphere, also known as “bad ozone,” is a gas produced by chemical reactions in volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides. Industrial emissions, car exhaust, and gasoline vapors are the main culprits.
Depending on geographic location and climate, ozone levels can spike during certain times of the year. Summer is one of the most affected seasons, due to higher levels of sunlight and hotter temperatures. These set off a chemical reaction with the pollutants, creating air that is harmful to breathe and causes damage to crops and vegetation. Continual exposure can lead to respiratory irritation, and may eventually lead to lung dysfunction and scarring.
Urban and suburban areas are typically hit the hardest with bad ozone; however, ozone has been known to spread up to 200 miles downwind from more polluted areas. Unfortunately, millions of Americans live in areas where national ozone standards are exceeded.
Air Pollution Health Concerns
Air pollution is certainly cause for public concern, specifically in relation to its effect on public health. Its impact depends on the degree of exposure and which toxins are more prevalent in the area.
Signs that you may be suffering from air pollution-related illness include asthma aggravation, respiratory issues, and skin irritation.
Some conditions can range in severity from a persistent cold to heart disease or even cancer.

Not only does air pollution affect the physical body, but it has also been linked to mental health conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Air quality also plays a role in the health of the environment.
- Air pollution has been shown to stunt vegetation growth, bringing once-thriving agricultural production to a halt.
- Smog or haze produced by bad ozone reduces plant access to sunlight, inhibiting its growth and ability to produce oxygen.
- Air pollutants also have a direct relationship with water quality, making water sources hazardous for drinking and wildlife.
What Can We Do?
It’s often alarming to stop and think about the effect air pollution can be having on our lives. However, some of these effects can easily be reduced or even reversed if the proper steps are taken. Since sustainable industries like solar energy and green construction have been on the rise, the U.S. has seen a drop in CO2 emissions.
On an individual level, there are a number of steps you can take to help reduce air pollution. These include:
- Turning off lights and electric appliances when not being used
- Switch over to energy efficient products like lightbulbs
- Carpool and ride the bus to work or school, or opt for bike riding or walking
- Limit gasoline spills with cars, lawn mowers, or other equipment
- Only run full loads of laundry or dishes
- Use eco-friendly cleaning products
- Make sure containers of cleaners, chemicals, or solvents are tightly sealed to avoid harmful emissions
- Join your community’s conservation and energy efficiency programs
Investigating sustainable technologies and supporting local environmental conservation efforts can go a long way towards making the air we breathe healthier and safer for future generations.
While we have a long way to go in cleaning up our air, there is hope because even small changes can make a big impact in reducing the amount of pollution we are exposed to on a day-to-day basis, cleaning up our planet, and improving public health in the long term.
For more information on the risks from air pollution, visit the Mesothelioma Cancer Alliance.

Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links that help support the GSG mission without costing you extra. I recommend only companies and products that I use myself.
Posted in: Eco Friendly Living, Health Concerns, Lifestyle